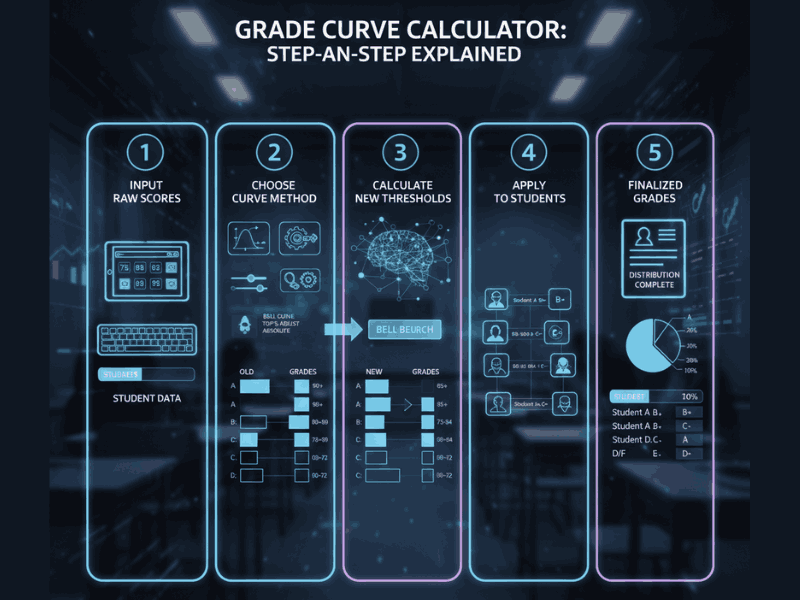
A grade curve calculator adjusts raw exam scores to improve fairness when a test is unusually difficult or uneven. Most grade curve calculators work by either adding fixed points, scaling scores, or applying a bell curve (normal distribution).
Simple curve formula (most common):
Curved Score = Raw Score + Curve Adjustment
Example:
If the highest score in class is 78 and the instructor wants the top score to be 90, the curve is +12 points.
A student with 65 becomes 77 after curving.
For automatic calculation, students commonly use tools like this Grade Curve Calculator:
👉 https://gradewisecalculator.com/grade-curve-calculator/
Introduction: Grade Curve Calculators
A grade curve calculator adjusts raw scores to a new scale using various methods, most commonly Linear Scaling (adding fixed points) or Root Function Curve (proportionally boosting lower scores). The goal is to correct for difficult assessments or align grades with a target distribution.
Common Method: Linear Scaling (Adding Fixed Points)
- Purpose: To shift all scores up by a consistent amount, often to make the highest raw score equivalent to 100% or to achieve a desired class average.
- Formula: Curved Score = Raw Score + Adjustment
- Where Adjustment = Target Max Score – Highest Raw Score (if aiming for 100% for the top score) or a fixed number set by the instructor.
- Example:
- Raw Scores: 60, 75, 85, 90 (Max Possible: 100)
- Highest Raw Score: 90
- Target Max Score: 100
- Adjustment: 100 – 90 = 10 points
- Curved Scores:
- Student A (60): 60 + 10 = 70
- Student B (75): 75 + 10 = 85
- Student C (85): 85 + 10 = 95
- Student D (90): 90 + 10 = 100
Common Method: Root Function Curve (Accelerated Scaling)
- Purpose: To provide a larger benefit to lower scores while still improving higher scores, but to a lesser degree. It stretches the lower end of the grading scale more significantly.
- Formula (using Square Root): Curved Score = SQRT(Raw Score / Max Possible Score) * Max Possible Score
- Example:
- Raw Score: 64, 81, 100 (Max Possible: 100)
- Curved Scores:
- Student A (64): SQRT(64 / 100) * 100 = SQRT(0.64) * 100 = 0.8 * 100 = 80
- Student B (81): SQRT(81 / 100) * 100 = SQRT(0.81) * 100 = 0.9 * 100 = 90
- Student C (100): SQRT(100 / 100) * 100 = SQRT(1) * 100 = 1 * 100 = 100
Process:
Output: Display the new, curved scores.
Input: Enter raw scores and the maximum possible score.
Select Method: Choose the desired curving algorithm.
Calculate: Apply the chosen formula to each raw score.
What Is a Grade Curve Calculator?
A grade curve calculator is a tool that applies a mathematical adjustment to exam or course scores. It does not randomly increase grades. Instead, it follows a defined method chosen by the instructor or institution.
Grade curve calculators are commonly used in:
- Universities and colleges
- Competitive courses (engineering, medicine, law)
- Large lecture classes
- National standardized exams (in limited forms)
The goal is fairness, not inflation.
How a Grade Curve Calculator Works (Step by Step)
A grade curve calculator works by comparing student performance against a reference point. That reference can be the highest score, class average, or a statistical distribution.
Step 1: Collect Raw Scores
All student scores from the exam or course are entered into the system.
Step 2: Choose the Curve Method
The instructor selects how grades will be curved:
- Fixed-point curve
- Linear scaling
- Bell curve (normal distribution)
Step 3: Apply the Formula
The calculator adjusts each score based on the chosen method.
Step 4: Generate Curved Grades
Final grades are recalculated and reassigned.
Students can preview outcomes using tools like the grade curve calculator linked above.
Common Grade Curving Methods Explained
1. Fixed-Point Curve (Most Common)
This is the simplest and most transparent method.
Formula:
Curved Score = Raw Score + Added Points
Example:
- Raw score: 68
- Curve: +10
- Final score: 78
This method is often used when the exam average is much lower than expected.
2. Linear Scaling Method
Here, all scores are stretched proportionally so the highest score reaches a target value.
Formula:
Curved Score = (Raw Score ÷ Highest Score) × Target Score
Example:
- Highest score: 80
- Target score: 95
- Student score: 64
(64 ÷ 80) × 95 = 76
3. Bell Curve Grade Calculator (Statistical Method)
A bell curve grade calculator uses normal distribution, placing most students around the class average.
Key features:
- Average becomes a B or C
- Few A’s and few F’s
- Grades depend on relative performance, not raw marks
This method is common in competitive programs but less transparent to students.
Grade Curve Calculator Example (Real Case)
Before Curve
| Student | Raw Score |
|---|---|
| A | 82 |
| B | 74 |
| C | 65 |
| D | 58 |
Highest score = 82
Target top score = 92
Curve = +10
After Curve
| Student | Curved Score |
|---|---|
| A | 92 |
| B | 84 |
| C | 75 |
| D | 68 |
This simple adjustment can change pass/fail outcomes significantly.
Why Professors Use Grade Curves
Grade curving is not about favoring students. It is used because:
- Exams may be harder than planned
- Class performance may cluster too low
- Different sections need consistency
- Academic standards must be maintained
Students often use online calculators to estimate results before official grades are released.
User Guide: How to Use a Grade Curve Calculator
- Enter your raw score
- Enter highest score or class average
- Select curve type
- Apply curve
- Review estimated grade
For fast estimation, students rely on tools like
👉 Grade Curve Calculator: https://gradewisecalculator.com/grade-curve-calculator/
Tips to Benefit from Grade Curving
- Always aim above class average
- Don’t rely on curves as a strategy
- Understand grading policy early
- Track relative performance, not just marks
- Ask professors which curve method they use
Frequently Asked Questions
Does a grade curve always increase grades?
No, a grade curve does not always raise scores. In most cases, it increases grades when an exam is harder than expected. However, if overall class performance is unusually high, a curve may have little effect or, in rare situations, slightly lower relative grades.
Is bell curve grading fair for students?
Bell curve grading is considered fair in competitive environments because it compares students against each other rather than absolute marks. However, it can feel unfair in strong classes where many students perform well but only a few can receive top grades due to distribution limits.
Can I calculate my curved grade exactly before results?
You can estimate your curved grade only if the instructor clearly states the curve method used. Without knowing whether it’s a fixed-point, scaling, or bell curve method, calculators provide close estimates but not guaranteed final results.
Do all universities allow grade curving?
No, not all universities permit grade curving. Some institutions follow strict percentage-based or criterion-based grading policies. Whether curving is allowed depends on university regulations and individual course guidelines.
Does grade curving affect GPA?
Yes, grade curving directly impacts GPA because it changes final letter grades. Once grades are curved and finalized, the updated grade points are used in GPA or CGPA calculations for that semester or academic year.
Is grade curving used in schools as well as universities?
Grade curving is mostly used in colleges and universities, especially in large or competitive courses. It is uncommon in primary and secondary schools, where grading is usually based on fixed percentage ranges.
Can professors curve grades for individual students?
Generally, no. Grade curving is applied to the entire class to maintain fairness and consistency. Adjusting grades for individual students is usually handled through re-evaluation or special academic consideration, not curving.
Is grade curving allowed under academic policies?
Yes, grade curving is allowed when it follows institutional academic policies. Universities typically outline acceptable grading practices, and instructors must apply curves in a transparent and consistent manner.
Using tools like an online grade curve calculator gives students clarity—but consistent effort always matters more than any curve.